Innovative Robotic Assited Knee Replacement for Better Outcome
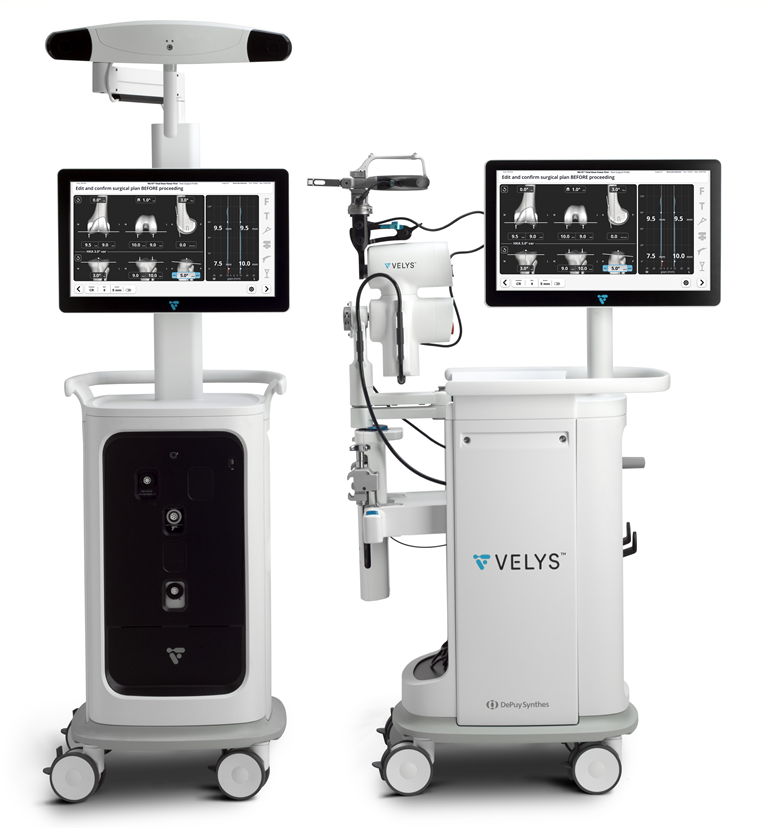
What is VELYS™ Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement (Generation 4)?
VELYS™ Robotic-Assisted Solutions (VRAS) is a tool used by orthopedic surgeons to assist in knee replacement surgeries, making the procedure more accurate, efficient, and faster. The latest Generation 4 version is compact and easy to move, giving surgeons flexibility in its use. The robot can be controlled precisely to ensure it moves as directed. The VELYS™ system features three key technological advancements:
3 Key Advantages of VELYS™ Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement (Generation 4)
1. No need for a CT scan: This reduces radiation exposure, increasing patient safety while also shortening preparation time and the duration of surgery.
2. Advanced imaging and analysis technology: Using preoperative imaging, measurements taken during surgery, and the patient’s anatomical structure, the robot assists in planning to perform the procedure. The system provides real-time updates via a camera, helping the surgeon adjust the original knee joint, control tissue and ligament tension, and position the implant for the most optimal fit. This real-time data enhances surgical precision, leading to improved outcomes and potentially extending the longevity of the knee implant.
3. Precision and accuracy: The robot ensures the knee implant is positioned and locked within a precision range of 0.5 mm or 0.5 degrees. It also controls the movement of surgical tools and the implant to avoid misalignment, reducing damage to surrounding tissues, ligaments, and muscles. These results in quicker recovery, less pain, and faster rehabilitation compared to traditional methods, cutting down both recovery time and hospital costs.
Who is a Suitable Candidate for Robotic-Assisted Knee Replacement?
Robotic-assisted knee replacement is suitable not only for elderly patients suffering from age-related osteoarthritis or knee degeneration due to injury but also for those with rheumatoid arthritis or previous knee replacements that have failed due to implant damage or decreased function.

.jpg)
